For indoor comfort, HVAC systems are essential. They comprise controls, ventilation, heating, and cooling technology that keep the air at optimal temperatures. Cooling systems produce cool air, and heating devices provide warmth.
The thermostats' control settings and ventilation guarantee the exchange of fresh air. Together, ducts and vents transport conditioned air, guaranteeing that residents have a comfortable interior environment.
Want to learn more about HVAC components? Keep reading to explore the core components of HVAC systems.
HVAC is an acronym for air conditioning, ventilation, and heating. It describes the integrated system that controls temperature, humidity levels, and air quality in houses, businesses, and other indoor places.
The HVAC system is essential to keeping the inhabitants' atmosphere cozy and healthful all year.
Heating: HVAC systems use a variety of appliances, including furnaces, boilers, and heat pumps, to provide warmth throughout the winter months. These systems produce heat, which is then dispersed throughout the structure via radiators or ducting.
Ventilation: To enhance air quality, ventilation entails exchanging air between interior and outdoor spaces. It restores oxygen levels and removes dampness, smells, and contaminants. Fans, vents, and air ducts are the tools ventilation systems use to move fresh air around and eliminate stale air.
Air conditioning: During hotter months, HVAC systems can also provide cooling options to control indoor temperature. The same ductwork used for heating is utilized to distribute cooled air, extracted from indoor air using air conditioners or heat pumps.
These systems cooperate and are frequently managed by a single control panel or thermostat. They provide the ideal indoor temperature and air quality by maintaining a steady and cozy atmosphere.
The size and complexity of HVAC systems vary according to the type of structure they are used in.
By delivering heating and cooling and ensuring proper ventilation all year round, they provide a substantial contribution to energy efficiency, indoor comfort, and general well-being.
Examining HVAC systems' components exposes a variety of heating technologies, including energy-efficient heating systems like electric heaters, heat pumps, and furnaces, all of which are essential for effectively supplying warmth.
In exploring heating components in HVAC, it is found that furnaces are typical HVAC system heating components. To produce heat, they burn fuel, like oil or natural gas.
The building's ducting or radiators are then used to disperse this heat. Contemporary furnaces integrate cutting-edge technology to enhance energy efficiency and provide accurate temperature regulation.
Every heating component has special benefits regarding cost-effectiveness, energy efficiency, and environmental compatibility.
It is easier to design HVAC systems that prioritize energy efficiency and environmental sustainability while meeting specific heating requirements when aware of these components.
In particular, HVAC systems' cooling components—air conditioners and refrigeration systems—are essential for maintaining efficient cooling solutions and pleasant interior temperatures in various settings.
Air conditioners are essential appliances that reduce heat and humidity to control indoor temperatures.
They function via the refrigeration cycle by using a refrigerant that absorbs heat from interior air and converts it to a cooler condition.
During the cooling process, refrigerant chemicals are compressed, condensed, expanded, and evaporated, eventually dissipating heat outdoors and circulating cooler air indoors.
While refrigeration technology serves particular cooling needs, it functions according to similar principles.
These systems, frequently seen in commercial spaces like warehouses and supermarkets, keep perishable goods fresh by maintaining lower temperatures.
To attain and maintain the precise temperature levels required for food storage, they use cutting-edge cooling technology with compressors, condensers, and evaporators, guaranteeing freshness and avoiding spoiling.
Refrigeration systems and air conditioners are two examples of effective cooling solutions.
They improve comfort by maintaining ideal interior temperatures in homes and businesses and make it easier to preserve items, guaranteeing their quality and prolonging their shelf life.
These cooling technologies are essential parts of HVAC systems that fulfill a wide range of purposes, from maintaining perishable goods to establishing comfortable spaces, greatly enhancing a variety of industries, and improving daily comfort.
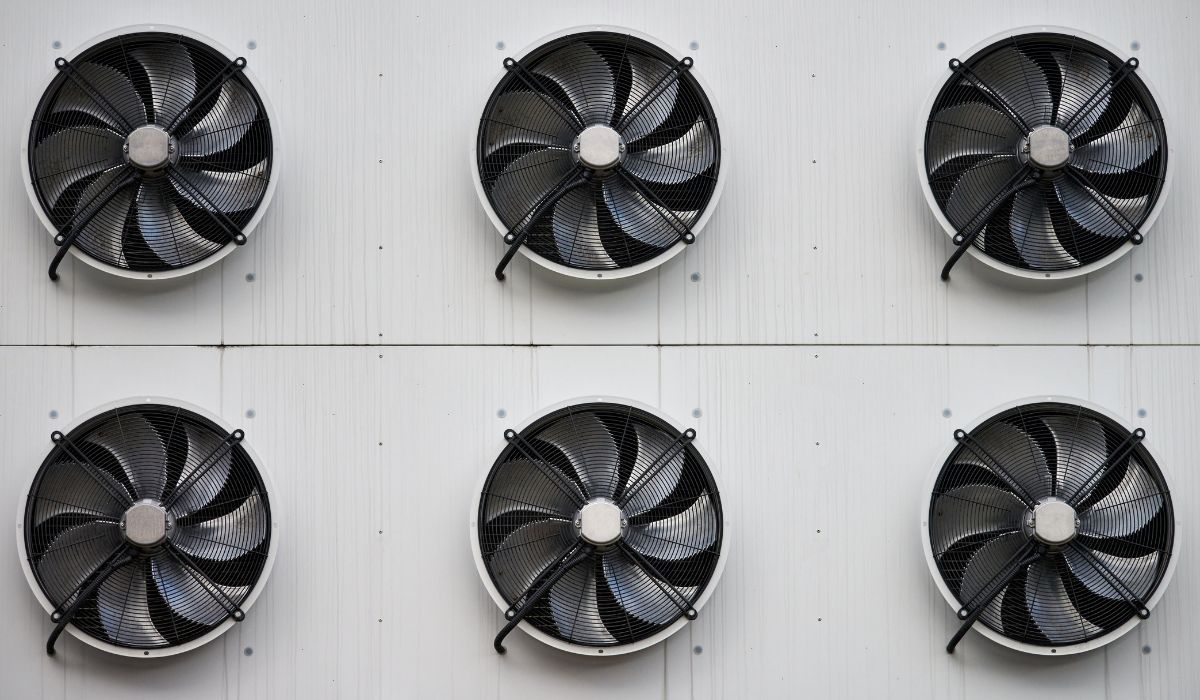

Ventilation technology is essential for improving air quality by exchanging stale indoor air with fresh outdoor air.
A number of parts, such as fans, air purifiers, and air ducts, play a major role in the efficient ventilation of HVAC systems.
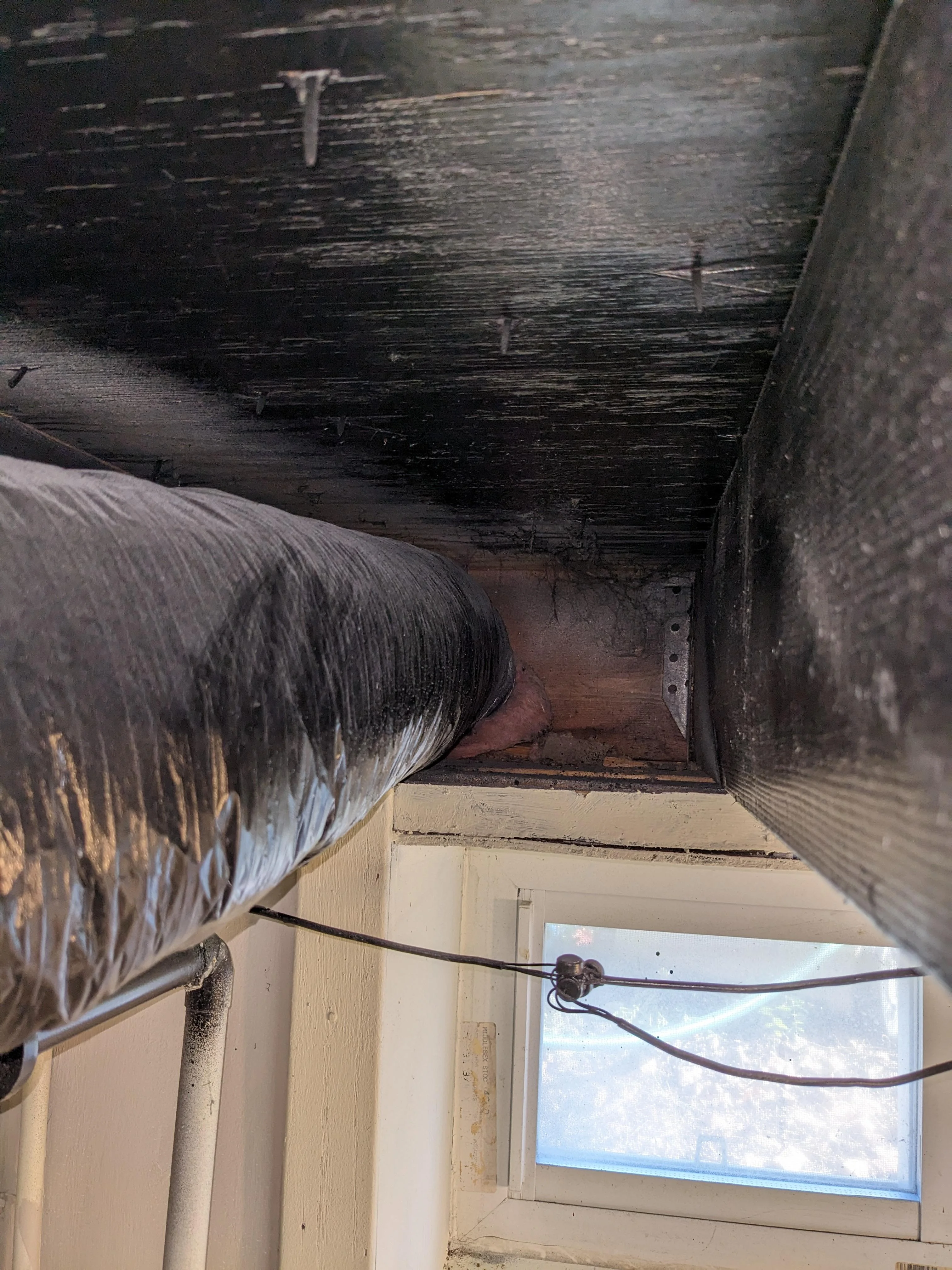

Efficient airflow is ensured by well-designed and maintained ductwork, which helps to prevent contamination and maintain air quality.
Kitchen and bathroom exhaust fans eliminate surplus moisture and smell, improving air quality and lowering the possibility of mold or mildew.

To drastically improve indoor air quality, they employ various filtration technologies, such as UV-C light or HEPA filters, to absorb and destroy contaminants.
Understanding ventilation components in HVAC aids in lowering the concentration of airborne contaminants, controlling humidity, and mitigating indoor air pollution.
In addition to making indoor spaces healthier and more comfortable, properly operating ventilation lowers the risk of allergies, respiratory problems, and other health problems linked to poor air quality.
To regulate temperatures and improve energy efficiency in both residential and commercial environments, smart HVAC controls and energy-efficient thermostat technology are essential:
Thermostats: The main point of contact between consumers and HVAC systems is the thermostat. These devices allow for exact temperature control by letting users define preferred temperatures.
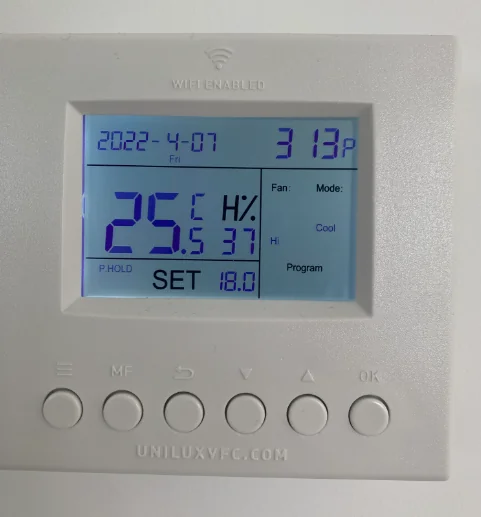
Advanced features like smart technology, remote access, and programmable settings are standard on modern thermostats.
With the help of programmable thermostats, users may plan temperature changes according to occupancy patterns, maximizing comfort and lowering energy use while the space is empty.
By learning users' preferences and modifying settings accordingly, smart thermostats further improve energy efficiency and offer extra benefits.
Control Systems: HVAC control systems are comprised of many equipment and technologies that are used to regulate and synchronize the operation of air conditioning, heating, and ventilation systems.

These systems control the distribution of conditioned air, fan speeds, and overall system performance. Additionally, they work with sensors and other HVAC parts to maintain the building's temperature precisely.
Zoning is a technique advanced control systems use to maximize comfort and energy efficiency by directing airflow to specific regions based on individual temperature requirements.
Managing HVAC with thermostats and control systems is essential. They greatly reduce energy use and allow customers to maintain pleasant indoor temperatures.
Building occupants can experience increased comfort and significant energy savings by utilizing programmable features, smart capabilities, and sophisticated control systems.
Ultimately, these technologies enable users to operate HVAC systems efficiently, guaranteeing peak performance and energy economy in residential and business environments.
In HVAC systems, well-planned distribution and ducting networks are essential for efficiently distributing warm or cooled air across buildings.
These elements greatly impact the system's overall performance, comfort levels, and energy efficiency.
Let us get into exploring ductwork and distribution components:

They reduce airflow resistance, which can lead to leaks and energy waste in poorly constructed or broken ducts.
The prevention of hot or cold areas by balanced airflow improves occupant comfort levels overall.
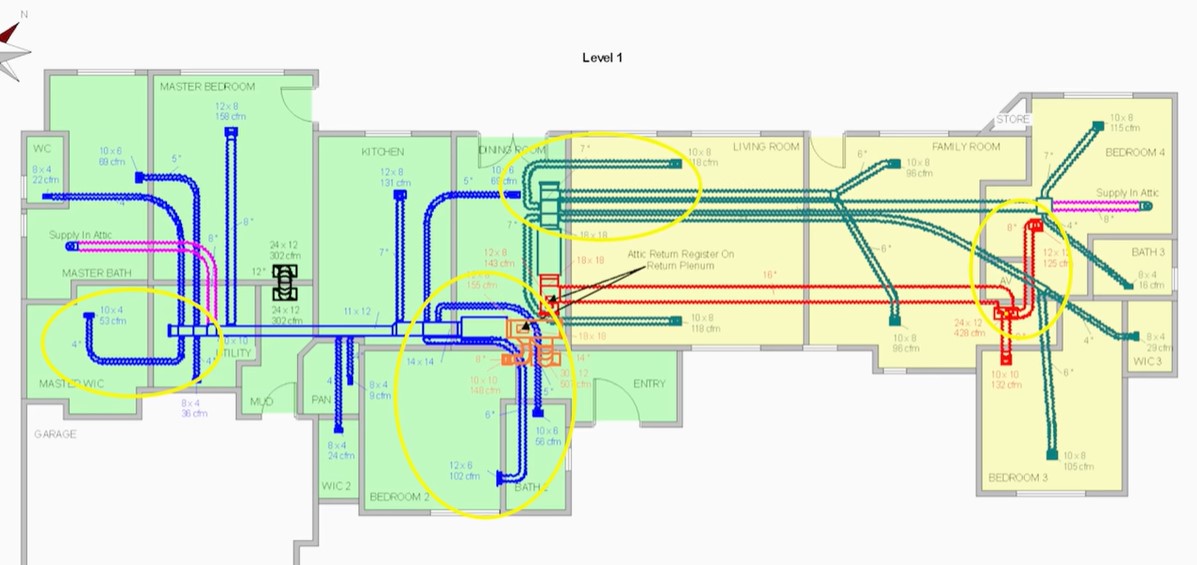
Achieving the best possible HVAC performance requires efficient distribution and ducting systems. By making certain that conditioned air always reaches every area of the building, they maximize energy efficiency and preserve a comfortable atmosphere.
Effective systems enhance airflow dynamics, lower energy use, and help create a comfortable and balanced indoor environment, giving tenants a consistent and enjoyable experience across the building.

Ensuring longevity through HVAC component maintenance requires routine maintenance. In addition to improving system performance, this preventive HVAC maintenance measure helps in sustainable climate control in both residential and commercial settings.
This keeps possible problems like decreased airflow or system failures at bay, ensuring the system runs at peak efficiency for the duration of its life.
Frequent maintenance keeps the system operating at peak efficiency, which lowers energy waste and related expenses.
This not only postpones the need for pricey replacements but also guarantees reliable performance over the long haul.
Homeowners and building managers can optimise system efficiency, reduce energy consumption, and extend the life of their HVAC units by making regular maintenance of HVAC components a priority.
In addition to ensuring comfort, implementing a maintenance schedule, performing inspections, cleaning or changing filters, and quickly attending to minor difficulties not only ensures sustainability in energy usage but also lowers the environmental effect and saves operating costs over time.
Final thoughts on HVAC components are that indoor comfort and efficiency in HVAC systems rely on key components such as heating units, cooling systems, ventilation, controls, and distribution systems.
These elements work harmoniously to regulate temperature, air quality, and airflow. A well-maintained HVAC system ensures optimal performance, delivering consistent comfort indoors.