Do you have questions about how many watts does a refrigerator use? Do not worry, keep reading to find answers to all your queries.
The power usage in refrigerators has a direct influence on energy efficiency and electricity prices, therefore understanding it is crucial. One of the few items in our houses that operates constantly is the refrigerator, which significantly raises our energy costs each month.
Homeowners may improve their home's energy efficiency by being aware of electricity expenditure and by using energy-saving appliances. In addition to using less power, efficient refrigerators maintain constant temperatures, assuring the safety of food.
This enables people to choose new appliances with knowledge since energy-efficient models not only lessen their impact on the environment but also result in significant long-term cost savings.
Exploring refrigerator power consumption also promotes sensible usage practices, such as adjusting thermostats to the ideal levels and reducing door openings, which further reduces the cost of electricity.
Read on to understand how refrigerators work and tips to reduce refrigerator energy use.

The complex but effective cooling mechanism that powers refrigerators depends on vital parts, including cooling systems and compressors. Recognizing refrigerators' roles in both food preservation and energy consumption is essential to understanding refrigerator functionality.
A refrigerator's functionality is to keep the atmosphere inside its sections cool and controlled. Compressors and cooling systems are used in a cycle to accomplish this. Here is a summary:
Compressors: The heart of a refrigerator's operation is its compressors. They are essential for preserving the optimum temperature. The heated air from within the refrigerator is sucked into the evaporator coils when food is placed inside.
The condenser coils are found on the rear or bottom of the refrigerator. The compressor then compresses a refrigerant gas (usually a form of Freon) and pumps it there.

Cooling Systems: As it passes through the condenser coils, the compressed refrigerant gas, which is now at high pressure and temperature, releases heat. The gas then condenses into a high-pressure liquid as a result.
After passing through an expansion valve, where it rapidly expands and transforms into a low-pressure gas, the liquid. The refrigerant rapidly cools down as a result of this expansion process.
Absorbing Heat: The evaporator coils inside the refrigerator compartments are then purged with the low-pressure, cooled gas.
The temperature inside the refrigerator decreases as it travels through these coils because they absorb heat from the interior. This procedure keeps the atmosphere for storing food consistently cool.
Now, when it comes to the role of compressors and cooling systems in power consumption:
To maintain a cold interior environment, refrigerators run continuously on compressors and cooling systems.
This procedure depends heavily on compressors, which also account for most of the energy the device uses. Users can choose energy-efficient refrigeration options to lower their electricity use by being informed about this functionality.

For households, calculating appliance power usage through the wattage and kilowatt-hours (kWh) of electricity used by the refrigerator is a useful exercise. It gives important information about monitoring energy consumption and enables people to choose items wisely.
Here is how you can gauge a refrigerator's power usage and why knowing this data is important:
Wattage Rating: Find the wattage rating of the refrigerator to get a baseline for calculating its power usage. Usually, the user handbook or a label inside the refrigerator will have this rating. It reflects the maximum amount of power the refrigerator can use when running normally.
Using a Wattmeter: You can use a wattmeter or a power meter if the wattage rating is not easily accessible. Simply connect the refrigerator to the meter, and it will show the current Wattage used.
Time Measurement: You need to know how long the refrigerator runs to calculate energy usage over a certain time frame. For instance, note how many hours the fridge runs each day if you want to figure out the monthly use.
Conversion: Since 1 kilowatt equals 1,000 watts, divide the measured or rated Wattage by 1,000 to convert it to kilowatts.
To calculate kWh: Multiply the number of hours the refrigerator runs by its kilowatt rating.
The equation is kWh = (Wattage in kW) x (Hours of Operation).
Now, you may be wondering why this information is valuable for homeowners. Let us walk you through it:
Cost Control: By understanding how much energy your refrigerator uses, you can calculate its effect on your monthly electricity payment. You may save utility bills by making informed judgments and monitoring your energy usage.
Energy Efficiency: Homeowners can use it to determine how energy-efficient their refrigerator is. Older models could use more energy, causing you to think about upgrading to a more energy-efficient appliance.
Appliance Maintenance: Abnormally high power usage may indicate a fault or poor functioning. Regular monitoring can alert the need for immediate maintenance or repairs, averting potential failures and additional energy loss.

Impact on the environment: Less energy use results in a smaller carbon impact. Understanding how much energy your refrigerator uses is in line with sustainable living principles.
Budget Planning: Budgeting for household bills is made easier by being aware of how much energy your refrigerator consumes. You can spend your money on power more wisely thanks to it.
Comparison Shopping: Understanding power consumption while shopping for a new refrigerator will help you compare models and select one that is both functional for your needs and energy-efficient.
Homeowners may manage their energy use, keep utility cost savings in check, and choose appliances in an environmentally friendly way by measuring the power consumption of their refrigerators in terms of Wattage and kWh. It's an important step toward effective and long-lasting house management.
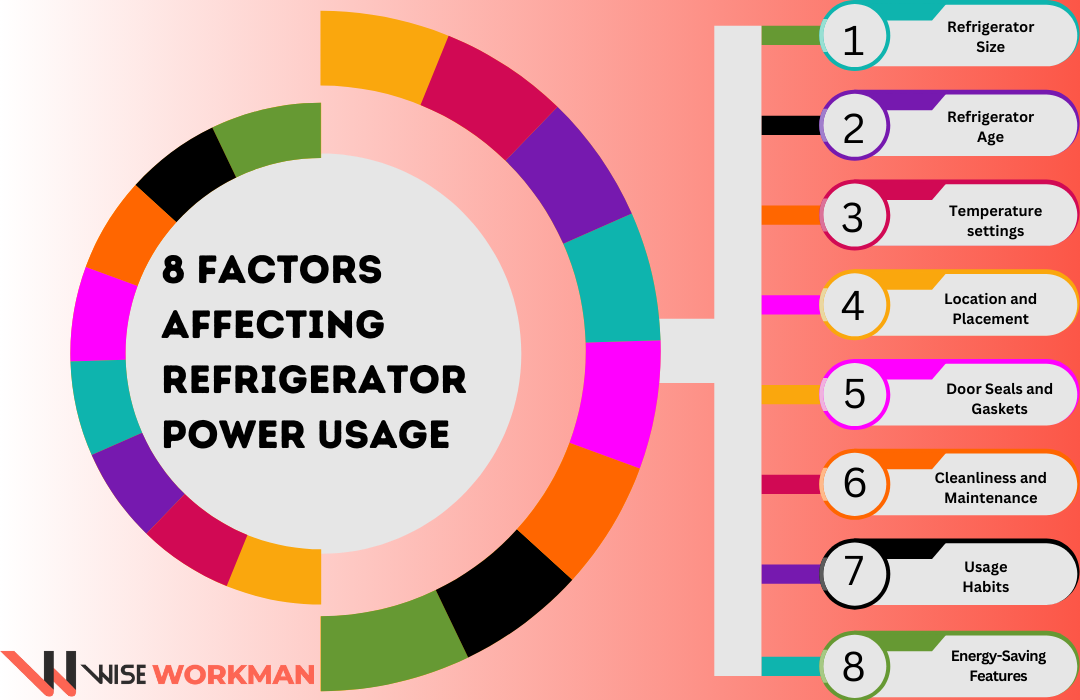
The energy consumption of a refrigerator is significantly influenced by several variables. Homeowners may maximize the use of their appliances and cut their energy expenses by being aware of these elements. Here are some determining energy efficiency factors to look out for:
Switching to an Energy Star-rated appliance can save a significant amount of energy.
Understanding influential factors in refrigerator power usage and controlling these energy-consuming elements for refrigerators can result in long-term energy savings of a significant amount.
By implementing energy-efficient habits, optimizing appliance settings, and ensuring that their refrigerators are maintained properly, homeowners may lower their electricity costs and lessen their environmental impact.
The average refrigerator energy consumption of a typical refrigerator can vary based on several factors, including size, wattage range, and brand. However, here is a general idea:
When it is actively running, a normal refrigerator typically uses between 100 and 800 watts of electricity. This can change depending on the model in question and its energy efficiency.
Now, let's explore how this average wattage consumption can vary based on size and brand:
| Type of Refrigerator | Power Usage Range (Watts) | Factors Influencing Power Consumption |
|---|---|---|
| Compact or Mini-Fridges | 100 - 400 | Smaller cooling areas and compressors contribute to lower power consumption. |
| Typical Domestic Refrigerators (Medium-sized) | 100 - 800 | Factors such as age, additional features, and energy efficiency affect power usage. |
| Larger Refrigerators with Ice Makers and Water Dispensers (e.g., side-by-side or French door models) | Up to 800 | Bigger size and added functionality lead to higher power consumption. |
The energy efficiency of various refrigerator manufacturers and models varies. While some manufacturers focus on energy-saving features, others might provide simpler models that use more energy.
The Energy Star certification on a refrigerator signifies that it has been tested and found to adhere to strict energy efficiency requirements.
Understanding brand differences reveals that energy star-rated refrigerators are built to use less electricity. As a result, they often consume less energy overall.
It's significant to note that contemporary refrigerators use less energy as a result of technological developments. Regardless of size or brand, older devices frequently use more electricity than their contemporary equivalents. Suppose you're thinking about buying a refrigerator.
In that case, it's a good idea to check the manufacturer's specifications for the appliance's precise Wattage to get an exact idea of how much energy it will use.
Therefore, a normal refrigerator's average wattage consumption can vary depending on things like size, brand, and energy efficiency. Smaller units use less electricity. However, larger versions with more features could need more watts.
Over time, estimating appliance energy use and choosing an energy-efficient refrigerator from a reliable manufacturer will help you use less electricity and pay less for utilities.

Enhancing refrigerator efficiency benefits the environment and lowers your electricity costs. Here is some helpful advice and tactics for homeowners to accomplish this:
The best temperature settings are to have your freezer at 0°F (-18°C) and your refrigerator at about 37°F (3°C). These settings minimize energy use while maintaining food safety.
To guarantee effective heat exchange, the condenser coils on the rear or bottom of the refrigerator should be cleaned at least once a year. To stop cold air leaking, inspect and replace worn-out door seals and gaskets.
Reduce the amount of time the door is open by organizing the food items. You may locate what you're looking for more quickly by labeling and classifying objects.
An overloaded refrigerator requires the compressor to work harder to circulate air. Keep it moderately but not overly stocked.
Make sure there is enough room around the refrigerator for effective ventilation. Keep it away from heat sources and bright sunshine.
Reduce how frequently you open the refrigerator door. Prepare ahead of time and pull everything out at once.
Before putting hot items in the refrigerator, let them cool to room temperature. The appliance may have to work harder because of hot objects raising the temperature inside.
A well-stocked refrigerator tends to keep the temperature more effectively. Don't crowd it to the point of restricting ventilation, though.
To avoid ice formation, which can limit efficiency, defrost your manual-defrost freezer regularly.
Use your refrigerator's energy-saving options, such as "power-saving mode" or "vacation mode," as necessary.
If your refrigerator is outdated and inefficient, think about upgrading it. More energy-efficient appliances are those that are more recent.
If the needs of your household have changed, switching to a smaller refrigerator can help save electricity.
Place a piece of paper between the door and the frame to periodically check the door seal. The seal could require adjusting or replacing if it's simple to remove.
To make sure they maintain the proper temperatures, place a thermometer inside your freezer and refrigerator. Configure settings as necessary.
Consider disconnecting any extra refrigerators that are hardly used, especially if they are older, less efficient models.
Homeowners may drastically minimize their refrigerator's energy use and enjoy cheaper power costs by implementing these energy-saving suggestions and lowering refrigerator power consumption techniques while maintaining food safety and convenience.
How many watts does a refrigerator use? It requires effectively monitoring and managing refrigerator power consumption not just a practical choice but a responsible one as well.
Here is a quick recap of energy management: homeowners may significantly lower their electricity costs and lessen their environmental effects by upholding energy-efficient habits.
The best temperature settings, routine maintenance, effective content organization, and thinking about switching to an energy-efficient model are some important lessons to remember.
These actions assist in finding a balance between maintaining food freshness and lowering energy waste. It's important to keep in mind that refrigerators are among the appliances in our homes that use the most energy, and over time, even little improvements may result in achieving saving goals.
Therefore, the conclusion on refrigerator energy consumption prioritizes refrigerator energy efficiency as a proactive way to contribute to both cost savings and a more sustainable future, benefiting both your wallet and the planet and ensuring efficient appliance use